The Overview of Patent Registration
Patent, you must be heard about it at least once in your life. Now a day it is very popular in the corporate world. It gives protection to the process and product. The requirement to get a patent is that your process or your product must be new in the market and they have a certain inventive step. Hence we can say that any product or process which is new in the market and have inventive step are eligible to get a patent. Through patent, making, using, selling, etc. of a product or process will be protected. The product or process for which the applicant is asking for the protection under Patent Act must be novel, and non-obvious; it must have some industrial application and enable. A patent application can be filed at the very first stage of research and development. The application can be in any form. It may be printed, handwritten, or typed. The language in which you can file an application for Patent Registration in India can be Hindi or English only.
One very important thing about the patent is that rejection of one claim doesn't means that all of your claims will be rejected. A patent can be filed outside India as well. It is possible because of Paris Convention. People prefer to take international patents because Indian patents will be applicable in India Only. As per section 3 and section 4 of the Indian Patent Act, there are certain things that cannot get patent or which are non-patentable inventions. Before filing for a patent of your product and process always make sure that your patent will not fall under the non-patentable inventions.
Different Patent Offices and their Jurisdiction
In India, there are a total of four patent offices from which one can claim Patent Registration. These four offices have different-different jurisdictions. Jurisdiction for the patent claim depends on the applicant’s residence or domicile, place of business, and the place where the invention actually originated. If in case there is no address or domicile in India then the address for service in India will also work. The list of different offices with their jurisdiction is given below-
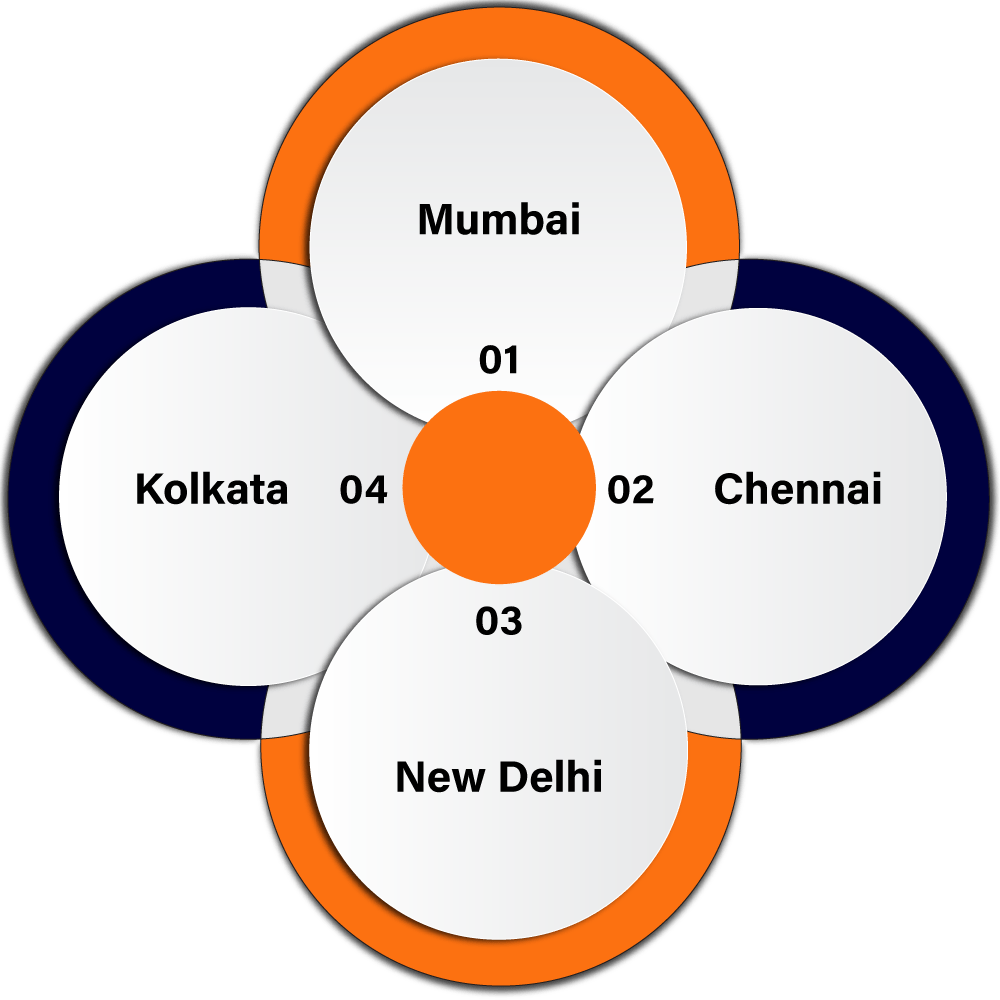
- Mumbai Office
- Chennai Office
- New Delhi Office
- Kolkata Office
Under Mumbai Office Maharashtra, Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, Goa, D&D, and the last Dadar and Nagar Haveli will come.
Under Chennai Office Andhra Pradesh, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Mysore, Pondicherry, Lakshadweep, and Minicoy
Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Jammu and Kashmir, Punjab, Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, Chandigarh, and Delhi will come under New Delhi Office.
The rest of India will come under the jurisdiction of the Kolkata Office.
Who can File Patent Registration?
There are certain categories of individuals and organizations that can ask for Patent Registration in India, some of them are given below-
- The true and first inventor of any product and process.
- The assignee of the true and the first inventor of any product and process.
- If true and the first inventor of the product or process dies, then in this situation both the assignee and his or her legal representative can claim for the Patent Registration.
Different Types of Forms Regarding Patent Filing
For the purpose of claiming Patent Registration, there are certain forms that one needs to be filling and present before the appropriate authority. Such forms are given below-
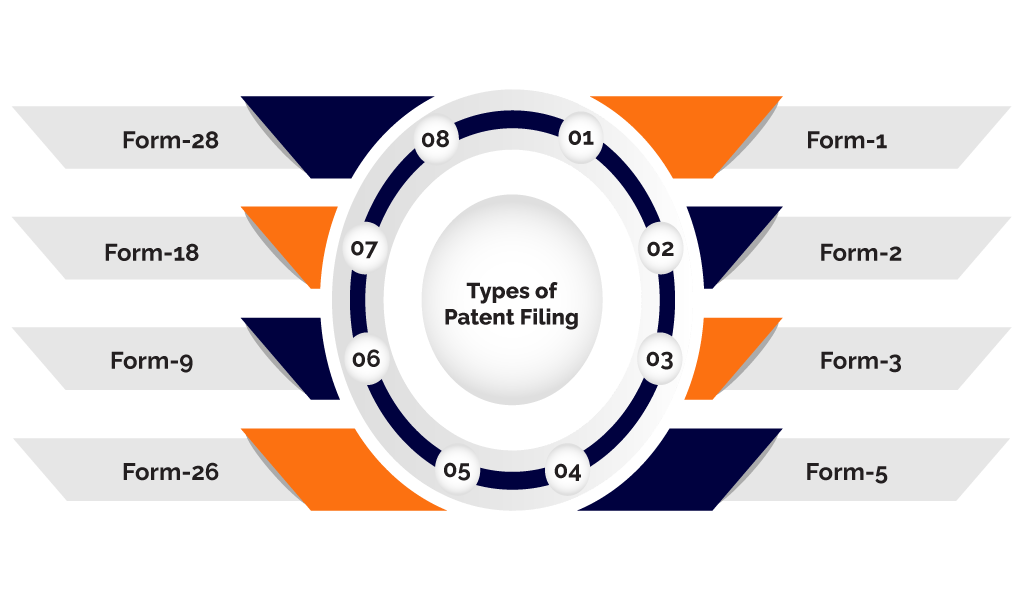
- Form-1
- Form-2
- Form-3
- Form-5
- Form-26
- Form-9
- Form- 18
- Form-28
This is one of the basic Forms related to Patent Registration. This form needs you to fill in the very basic information about the applicant such as name, address, etc.
Through Form-2 one needs to submit the title of the invention, then preamble to the description with the name, address, nationality, etc, of the applicant. This will reveal whether the patent application is provisional in nature or complete in nature.
This form is related to the statement and undertaking. Applicant must have to submit this form either with the Patent Registration application or within 6 months of such application.
This is used to declare the inventors of the subject matter sought to be protected by using the current application. What is not claimed in the patent application will remain disclaimed and it will remain open to the public. Hence don’t leave anything related to your product or process unclaimed.
This form is useful if you hire an attorney for filing a Patent Registration application on your behalf. This basically talks about ‘Power of Attorney.
Generally seeking a patent is a long-run process, but if you want it early then you can request the early publication with the help of Form-9
Examination request also needs to be filed as it is not an automatic process. It has to be done within the 48-months from the date of filing of the application. A person other than the applicant can also do the same on behalf of the applicant. The examination is always done whether the invention is patentable or not.
This particular form is related or particularly for the startups and small business entities. They need to file it.
Non-Patentable things as per Patent Act
Following are the things that are expressively Non-Patentable as per section 3 and section 4 of the patent Act-
- A machine that gives 100% efficiency, as it is scientifically impossible.
- Any machine which has been made for counterfeiting currency notes.
- Method of producing a plant by using a greenhouse.
- Surgical methods such as stitch-free incision for cataract removal.
- Curative methods such as removing plaque from teeth.
Benefits of Patent Registration
The benefits or advantages of obtaining registration under the Patents Act 1970 are as follows-
- Protection of Invention
- Sell or Transfer Patent
- 20 Years of Validity
- Helps in Growing Business
- Receive Royalties
- Monopoly
A Patent is an Intellectual Property Right that aims to protect one's creation or invention and restrict others to use it without obtaining the prior consent of the Inventor.
A Patent can easily be Sold, Transferred, or Franchised by the Inventor for generating revenue.
In India, a registered Patent remains valid for a period of 20 years, starting from the date of registration.
A registered patent will help the inventor to grow his/her business and will assist in raising capital for the business as well.
The Patentor can receive Royalties by licensing his/ her product to another company.
Once the businesses and investors obtain the Patent Registration, both can enjoy Market Monopoly as well as Competitive Benefits.
Requirements for Obtaining Patent Registration in India
In India, the key requirements for obtaining a Patent are as follows-
- Patentable Subject Matter
- Inventive or Non-obviousness
- Novelty
- Industrial Applicability
Section 3 and 4 of the Patent Act, include a list of Non-Patentable subject matter, which means if an invention falls under such a list, the same will not be eligible for a Patent and cannot get the Patent Registration.
The invention must not be obvious and simple in nature and needs to be considered by a skilled and experienced person. That means, it must be technologically advanced and economically profitable to be patented.
The term “Novelty” denotes that an invention must be of a unique nature and must not have been issued anywhere in India. That means the same should not be in the public domain before the filing of the application.
Industrial Applicability is necessary as per the requirement under Patent Act; the invention for which one wants to take Patent Registration must be practical and operational in the industries and public domain.
Rules for Obtaining Patent Registration in India
The rules for obtaining a Patent in India are as follows-
- The Fee for the Patent will be payable as per the First Schedule of the Patent Act;
- In case the applicant physically files the documents, then the authorities will charge an additional fee of 10%;
- The different modes of paying the fees are electronic means, Demand Draft, and Banker’s Cheque.
- The applicant will pay the fee to the Controller of Patents;
- If in case the application form is transferred from a natural person to any person other than a natural person, then the new applicant needs to pay the remaining amount;
- The case mentioned in point (e) will apply to Start-ups as well;
- It shall be taken into consideration that the fee once paid, will not be refunded back, unless, there is some excess amount paid to the Controller of Patents;
- The applicant needs to pay the fee in advance of the process of registration;
- In case the applicant withdraws the application filed prior to the issuance of the objection, then some amount of the fee paid will be refunded back to the applicant.
Different Types of Patent Registration Application
There are different types of Patent Registration Applications which are given below in detail-
- Ordinary Application
- Conventional Application
- PCT International Application
- PCT National Phase Application
Where both the filing and priority date are the same for the application and which denotes a fresh application that is filed under the patent Act, is called Ordinary Application.
The term “Conventional Application” denotes an application that is previously filed by the applicant in some other country and wants to file the same in India as well. Further, it shall be relevant to take into consideration that the applicant needs to file the said application within a period of 12 months, starting from the date of its first filing.
The term “PCT International Application” denotes an application that is filed by the applicant in multiple countries. One can file this application in a maximum of 142 countries. Also, the same will take around 30 to 31 months for claiming protection in each country, starting from the date of International Filing.
The term “PCT National Phase Application” denotes an application filed by the applicant in India just like in other countries for claiming protection. The applicant needs to file the same at the Indian Patent Office within a period of 31 months, starting from the date of International Filing.
Documents Required for Patent Registration
Necessary and important documents required for obtaining Patent Registration are as follows-
- Application for Patent Registration in Form 1;
- Proof of Right to file Patent Application. Further, this proof needs to be attached along with the application for Registration;
- In case the applicant does not have complete specifications, he/ she needs to file the provisional specifications. However, in the case of provisional specifications, the applicant requires to file the complete specifications within a period of 12 months in Form 2;
- Form 3 is mandatory for filing Statement and Declaration under section 8 of the Patent Act;
- Form 26 of the Patent Act talks about Power of Attorney, in case the application for Patent Registration is filed by the Patent Agent on behalf of the client.
- In the case of Biological materials, the applicant needs to obtain permission from the NBA (National Biodiversity Authority), before the issuance of the patent;
- In respect of the Biological Material, the applicant needs to mention the source of Geographical Origin under the Patent Act.
- The application for the Patent Registration must contain the signature of the Applicant, Patent Attorney, and Authorized Person as per the rules and regulations of the Patent Law.
- MSME or Start-up India Certificate, if in case any;
- The Applicant/ Agent needs to sign the last page of the Complete/ Provisional Specification;
Procedure for Obtaining Patent Registration
Follow the steps given below to get the Patent Registration-
- Establish a priority date for the patent application.
- File the application in the IPO.
- At this stage, you can file the request for early publication. (Optional)
- Publish patent application after filling all the requirements for the same within 18 months from the date of application.
- File a request for examination as it is not an automatic process within 48 months after the date of filing the patent application.
- Appropriate authority will examine the application.
- After the valid examination, the patent will be given, but if they find any problem in the application then they will issue an examination report. Then the response to the examination report will be given within 12 months. If not satisfied, it will result in the rejection of the patent.
Why Bizadvisors?
BizAdvisors is one of the platforms that work together to meet all of your legal and financial needs while also connecting you with dependable specialists. Yes, our clients are happy with the legal services we provide. They have continually regarded us well and provided regular updates because of our focus on minimizing legal requirements. Our clients can also keep track of the progress on our platform at any moment. Our knowledgeable professionals are here to answer any queries you may have concerning the Patent Registration process. BizAdvisors will make sure that your interactions with professionals are pleasant and smooth. Following are the reasons one should choose Bizadvisors-
- BizAdvisors is one of the many platforms which coordinate to fulfill all your legal requirements.
- It connects you with a team of expert professionals who can help you in every possible way.
- Its focus is on simplifying the legal requirements for the client.
- If you have any questions regarding Patent Registration we are just one phone call away.
- We have a very dedicated team that is ready to help you and guide you.
- Our mission is to create a hustle-free and easy-to-use system for the concerned consumers of our services.
- We give you reliability and trust.
- We make sure that we will provide you with the best services and can satisfy you with our quality work.
The term “Patent” denotes one of the pillars of Intellectual Property rights (IPR), and it is a right granted by the government to the inventor of his/her invention. Further, the term “right” includes the authority to make, sell, use, and import the product or process and restricts others from doing the same. It is governed and administered by the Patent Act 1970 and Patent Rules 1972 and remains valid for a period of 20 years. Moreover, the authority to manage the application for Patent Registration is with the Patent Office, Controller General of the Patents, Designs, and Trade Marks. In India, any individual or business entity that wants to protect and secure an idea or invention can apply for a Patent. The term “Invention” includes both the new product and new process. Also, a natural person who is an assignee under the Patent Law and claims to be the true and first inventor of the art/ research has the right to make such an application. The Legal Representative of a deceased person (who immediately before his death was entitled to make an application for Patent Registration) can file for a Patent as well. Patent increases your brand value in the market.
FAQs Regarding Patent Registration
In a very easy language, we can say that a patent is a protection given to a product and process which are new and have inventive steps.
This is one of the basic Forms related to Patent Registration. This form needs you to fill in the very basic information about the applicant such as name, address, etc.
Following are the things that are expressively Non-Patentable as per section 3 and section 4 of the patent Act-
- A machine that gives 100% efficiency, as it is scientifically impossible.
- Any machine which has been made for counterfeiting currency notes.
- Method of producing a plant by using a greenhouse.
- Surgical methods such as stitch-free incision for cataract removal.
- Curative methods such as removing plaque from teeth.
 9559179325
9559179325 9559179325
9559179325 9559179325
9559179325











