Overview of GMP Certification
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practice, and it is a word that is used around the world to describe the control and management of pharmaceutical product manufacturing, testing, and overall quality. It establishes a set of guidelines for the quality assurance methodology. GMP accreditation ensures that items are manufactured in accordance with industry standards.
The Commissioner of the Food and Drug Administration has authorized the Joint Commissioner to sign and issue certifications under the WHO-GMP certification programme. Documentation, record keeping, employee qualifications, sanitation, cleanliness, equipment verification, sanitation, complaint handling, and process validation are all covered by GMP certification.
GMP criteria are not unusual in any way; they are open-ended and simple to apply, and they provide manufacturers the freedom to select how to efficiently implement the essential controls on their own.
What is the Goal of Goods Manufacturing?
The major goal of GMP is to limit the amount of risk associated in the manufacturing of pharmaceuticals. Pharmaceutical items carry risks such as:
(a) unexpected uncleanliness in the product can have a negative impact on one's health and even lead to death;
(b) incorrect labels on containers implying that the patient is taking the wrong medicine,
(c) too much active or too little ingredient,
(d) ineffective treatment or adverse effects, and so on.
GMP has a lot of jurisdiction, including covering all parts of manufacturing, from raw materials to specifics about locations and equipment to employee training and personal cleanliness. It contains all of the information on the operations that result in the finished product and may have an impact on its quality.
What are the GMP Guidelines and How Do They Affect Certification Holders?
The World Health Organization (WHO) has established several manufacturing best practices recommendations. Several countries have created their own GMP requirements based on WHO GMP. Others, such as the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN), the European Union, and the Pharmaceutical Inspection Convention, have met their requirements.
GMP requirements demand a high-quality approach to production, allowing businesses to reduce or eliminate contamination, misunderstandings, and errors. This protects the customer from purchasing an item that isn't enticing or even dangerous.
Most GMP requirements are highly broad and open-ended, allowing each manufacturer to determine how best to implement the necessary controls. This provides a lot of flexibility, but it also requires the producer to decode the requirements in a way that makes sense for each specific firm.
What Are the Advantages of Obtaining GMP Certification?
GMP norms and procedures are followed by all pharmaceutical and medical device firms, however some have developed their own guidelines in accordance with local regulations.
- Empower certification holders to choose great creation,
- Timely identification of manufacturers and management issues,
- Adherence to key laws and guidelines
- Improve overall trustworthiness and public perception;
- Reduce product quality and safety risks;
- Consumers will have more faith in your items as a result of this.
- Reduces operating expenses by reducing rework and fines for non-compliance.
- Increases export opportunities,
- Reduces inspection duplication,
- Saves money.
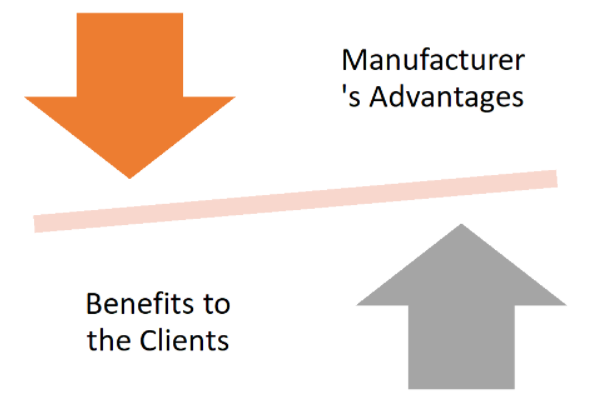
Manufacturer's Advantages
One of the main advantages is that the manufacturer's quality systems and quality compliance have greatly improved. These gains were visible in the months coming up to GMP certification and continued in the years following certification.
Benefits to the Client
Customers are more likely to change their oversight of GMP-certified manufacturers. Customers are aware that in order to be certified, the manufacturer must have mechanisms in place and offer proof that non-conformance and modifications that necessitate customer notification are handled properly. This assurance is often gained through a rigorous, multi-day audit of a manufacturer as part of a certification audit programme, rather than a one-day supplier audit conducted by pharma companies.
What Documents Are Necessary for GMP Certification?
The required documents are as follows-
- Name of the applicant, including address, phone, fax, and e-mail.
- Manufacturing License Copies
- List of items that have been approved.
- Master file for the site (as specified under WHO TRS 823).
- Information about the Finished Formulation: -
- Become an expert in manufacturing formulas and processes
- Specifications for the finished product and the method of analysis
- Stability study evaluation (accelerated and real-time) for three batches, including batch size, batch number, production date, expiration date, stability study condition (accelerated/real-time), and more.
- Compile a validation report for each of the three batches.
- Report on the analytical method's validation.
- List of technical personnel, including their qualifications, experience, and status of approval.
- The following is a list of the equipment and instruments that will be used.
- Sops and stps are listed below.
- Layout of a manufacturing plant.
- Water system schematic diagram with circulation loop and MOC.
- A summary of the product (as per Format B).
- Rule 158B of the Drugs and Cosmetic Rules, 1945, requires proof of safety and effectiveness.
- Undertaking to comply with domestic legislation such as the Drugs and Cosmetics Act of 1940 and Rules thereunder, the Drugs and Magic Remedies (Objectionable Advertisements) Act of 1954 and Rules thereunder, and so on.
What is the GMP Certification Procedure?
The procedure for GMP Certification are as follows-
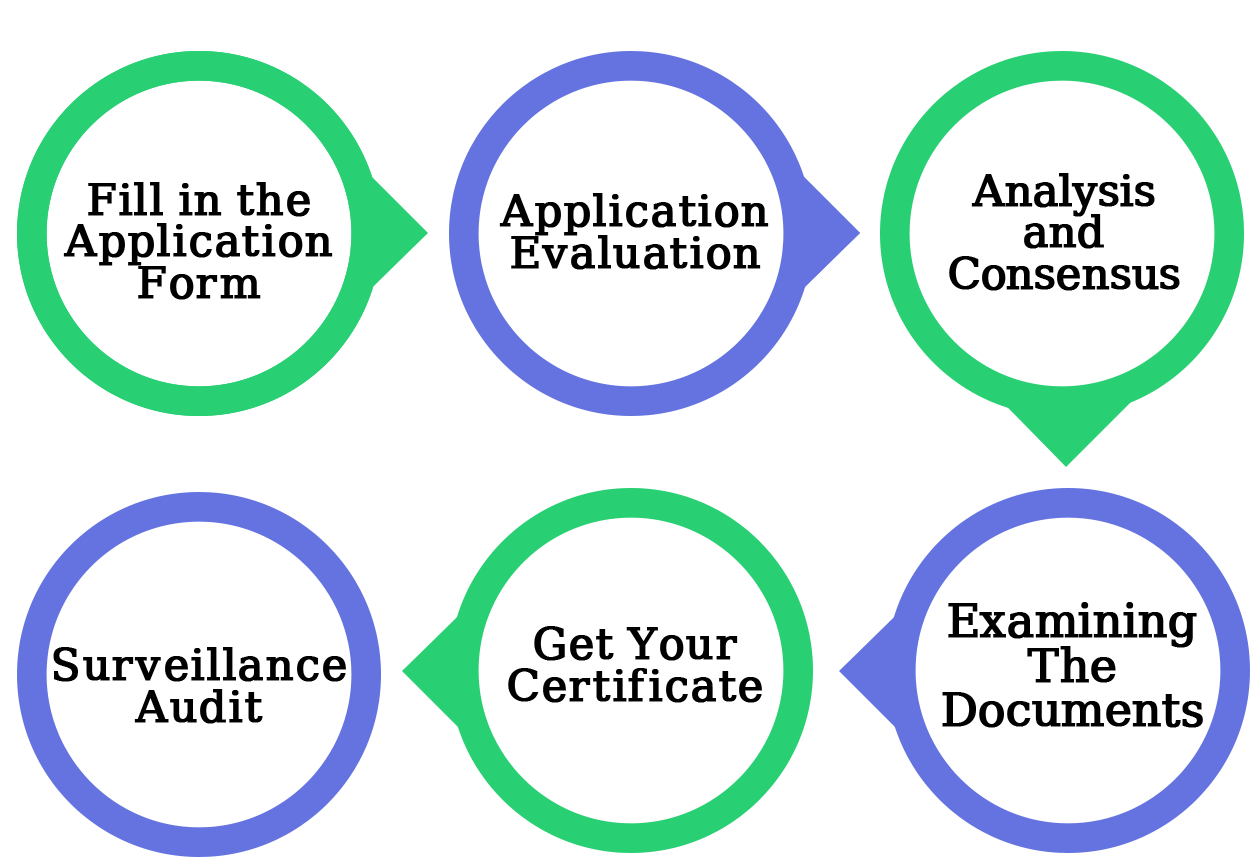
Application
This is the first stage in obtaining GMP certification; the application asks for some basic information about the company. The certification authority must accept the application and must record or maintain all of the data in the GMP database.
Application Evaluation
The panel will review the application to ensure that the consistency requirement has been met.
Analysis and Consensus
Give the value citation to play out the Gap Analysis after the document audit to cover all the provisos and areas of the quality rules. The Gap Analysis is used to determine how well an organization has organized and completed tasks.
Examining the documentation
Examine the organization's paperwork to ensure that it satisfies the compliance requirement.
Stage-1
- Conduct an audit
- Conduct a survey
- Rejuvenating Activities
- Double-check
Calculate the consistency requirement for your organization's recorded approach and strategies.
Then, go over your administration structure's documentation to ensure that the consistency requirements have been met.
The non-similarity is in charge of corrective actions. It must be made at the time of noncompliance.
Examine the establishment's documentation to ensure it meets the appropriate standards.
Stage-2
- Conduct an audit
- Remedial Action
- Double-check
The inspector verifies that the organization is operating as it should be based on its documentation, the examiner of the authoritative body identifies non-compliances, and finally, the reviewer provides an opportunity to correct the non-compliances. Then, according to the association's report, assess the execution technique.
If there is any non-similarity, a corrective action must be taken.
Your representatives will verify work directions before overseeing the execution process.
Certification is given.
The Certification Body will provide a compliance certificate that will be valid for a long period.
Audit of Surveillance
The purpose of the surveillance review is to ensure that the organization complies with the administrative framework's requirements. Every six months or one year after the certificate is given, an observation evaluation must be completed.
What are the Consequences of GMP Non-Compliance?
When you operate in the manufacturing industry, you need to be compliant and follow excellent manufacturing procedures. It not only assists you in producing a high-quality product, but it also promotes consumer and environmental health. What happens, however, if you don't follow GMP guidelines?
Let’s take a glance at the consequences of the same.
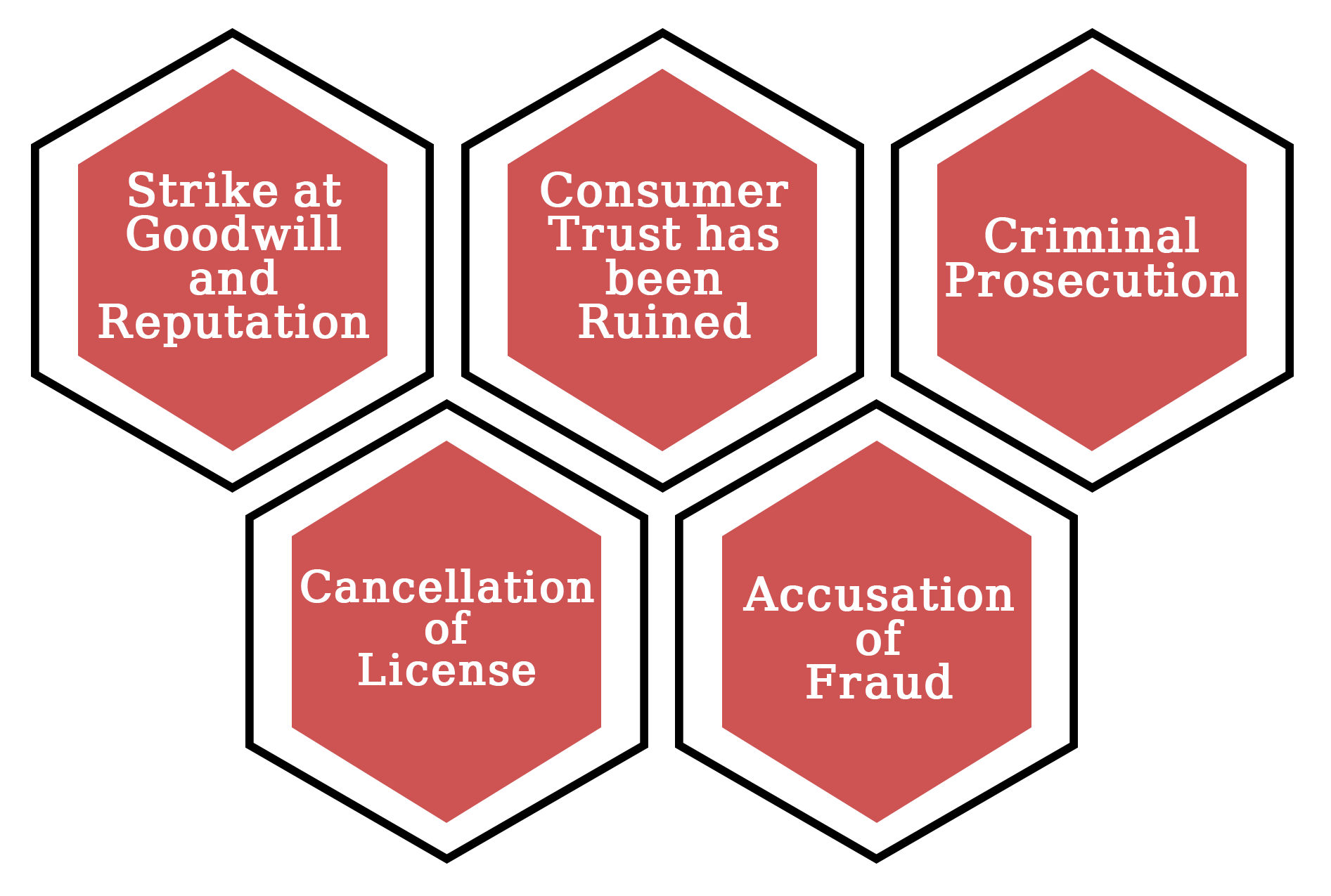
Strike at Goodwill and Reputation
The reputation of every firm is crucial. It's critical to consider how you acquire customers, build product loyalty, and keep people coming back to you. When you don't follow proper production processes, the first thing that suffers is your reputation. Customers who do not trust a manufacturer will not purchase your products.
Consumer Trust Has Been Ruined
The guiding idea of good manufacturing procedures is in place to keep your clients secure. Consumers will quickly lose faith in your product if you do not follow the recommendations. However, the consequences are far more serious than merely a business stumbling block.
Criminal Prosecution
The FDA, which grants certificates under the WHO-GMP certification programme, has the legal authority to confiscate a medicine and halt production through a court order. The Departments of Justice and Health and Human Services also have the authority to take action against any manufacturing company that violates good manufacturing practises if the circumstances warrant it.
Cancellations of licences
When dealing with manufacturing, there are a plethora of permits to consider. From building permits to licenced physicians to facility licencing, you'll need everything. If you don't follow the requirements for good manufacturing procedures, your job, your facility, and your doctors' licences could all be jeopardised.
Accusation of Fraud
Fraud charges may be filed if appropriate manufacturing processes are not followed. This can result from errors such as mislabelling components or amount, as well as failing to advertise a product in accordance with GMP rules. When a manufacturing firm is accused of fraud, the ramifications can be devastating.
When it comes to labelling and branding methods, the GMP requirements expressly target fraud. Failure to follow these recommendations can result in serious consequences.
What are the fundamental principles that GMP Guidelines want to follow?
- The manufacturing zone of a pharmaceutical assembly office must be kept clean and sanitary. Controlled environmental conditions should be maintained to avoid cross contamination of food or medicinal products with adulterants that could make them unsafe for human consumption.
- The manufacturing process is clearly defined and managed. To ensure consistency with specifics, each method must be approved.
- The manufacturing process is monitored, and any changes to the procedure are evaluated. Changes that have an impact on the medication's nature are approved as needed.
- Instructions and procedures must be written in a straightforward and unambiguous manner. Document procedures must be conducted by administrators.
- During the manufacturing process, records must be kept that demonstrate all of the actions required by the stated procedures and instructions, either manually or via instruments. Furthermore, all deviations must be explored and recorded.
- Records of manufacture (including distribution) are kept in a readable and accessible format, allowing the whole history of a batch to be traced.
- Complaints about things must be examined, and appropriate action must be implemented to address the substandard products and prevent recurrence.
In the pharmaceutical sector, GMP is followed.
GMP refers to a system of rules, rules, and procedures that govern the processing of drug substances and products, medical equipment, medical product categories in vivo and in vitro, and food items. The term GMP refers to pharmaceutical product production supervision and management, as well as quality control monitoring.
Everyone in the pharmaceutical sector should understand why GMP requirements are necessary, with the goal of preventing disasters.
Why Choose Us

Free Legal Advice

Transparent Pricing
On Time Delivery
Expert Team

Money Back Guarantee

200+ CA/CS Assisted

Lowest Fees

Easy EMIs
Frequently Asked Questions
The Commissioner of the Food and Drug Administration has authorised the Joint Commissioner to sign and issue certifications under the WHO-GMP certification programme. GMP certification is granted following the completion of a GMP examination of a producer following GMP rules. When sufficient paperwork on the examination follow-up is produced, the authenticity is granted.
An approved individual within the organisation seeking confirmation must submit the application for GMP certification. A Production Manager, a Quality Assurance Manager, a Quality Control Manager, or the MD are examples of people who have responsibilities.
GMPs are the practises that must be followed in order to comply with the rules set forth by the offices that oversee the approval and permitting of the manufacture and distribution of food and beverages, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, dietary supplements, and clinical devices.
- The ‘Current Good Manufacturing Practice' recommendations established by the US Food and Drug Administration are referred to as CGMP (FDA).
- GMP (Good Manufacturing Practice) is a framework for ensuring that things are provided reliably and that quality standards are followed.
 9559179325
9559179325 9559179325
9559179325 9559179325
9559179325











