Overview of FEMA Compliance
The Foreign Exchange Management Act serves as a guiding rule for regulating the flow of cash from abroad to India and vice versa. The act was passed in 1999 and, in addition to regulating finances, it also lists FEMA compliances that a corporation must follow.
This law aided in the smooth operation of cross-border trade, promoted foreign investment, increased the transparency of international financial operations, and improved the balance of trade payments.
Globalization and the rapid rise of international trade investments have increased the importance of FEMA filing. Furthermore, to keep a lid on sectoral caps, investment caps, and avoid Foreign Exchange Management Act non-compliance penalties.
As a result, it is critical for businesses to follow FEMA's guidelines and regulations. Furthermore, this method can help to smooth international corporate activity and manage regulatory liabilities more effectively.
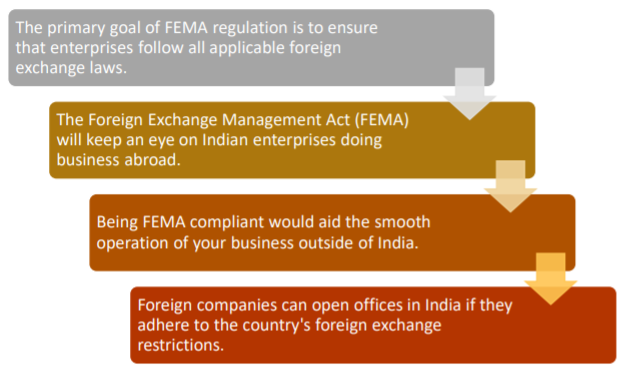
FEMA's Compliance Objectives
To conduct business in India, all transactions must adhere to the applicable foreign exchange laws. All services must be compatible with FEMA, from opening a bank account for an NRI to resolving issues under FEMA.
Why is FEMA compliance required?
Types of Services Offered- FEMA Compliance
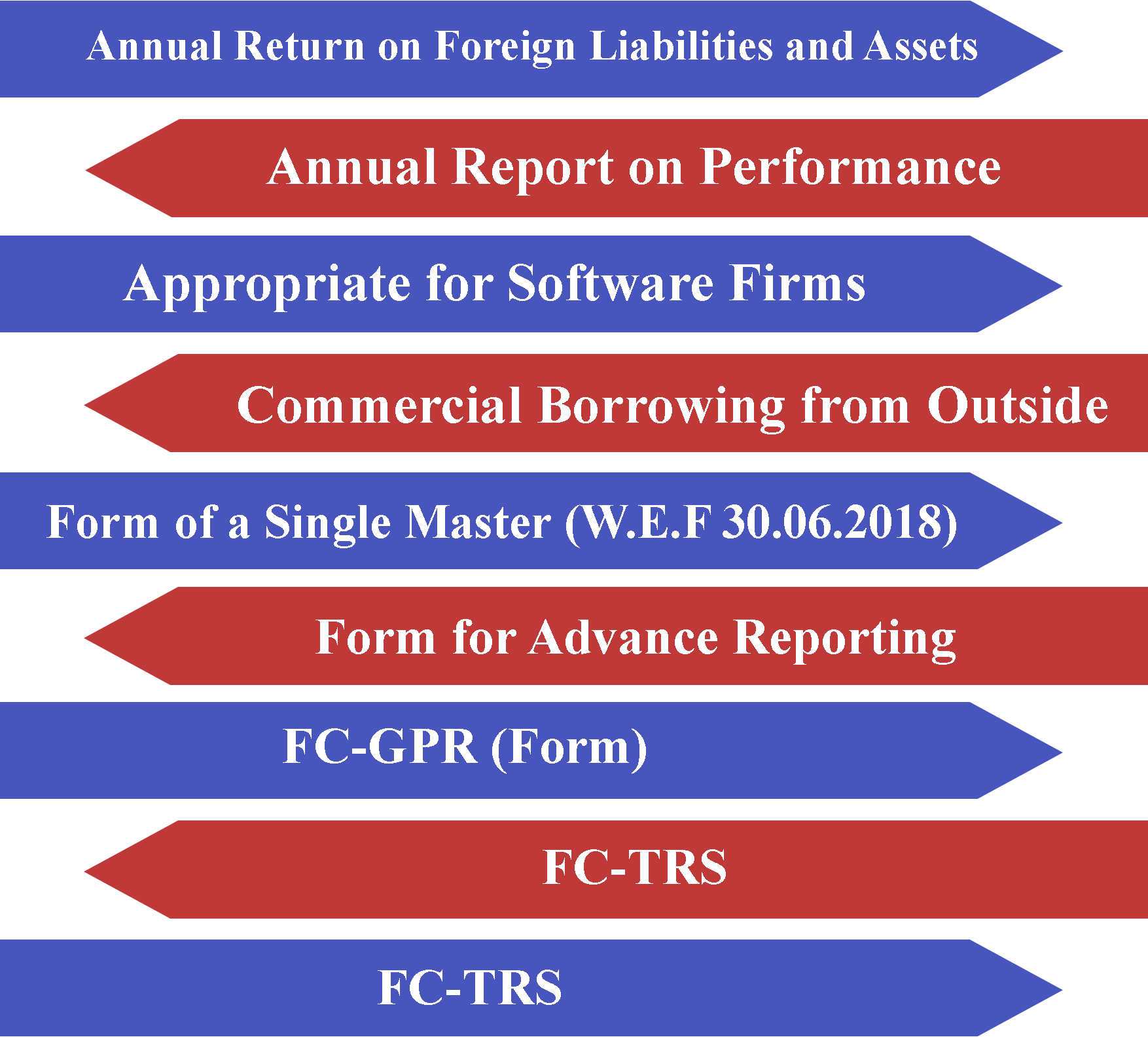
Under the rules of the FEMA Annual Return on Foreign Liabilities and Assets, there is a list of significant compliance that must be followed.
Annual Return on Foreign Liabilities and Assets
An Annual Return for Foreign Liabilities and Assets must be filed by all India-based firms that received FDI or made ODI in any previous year, including the present year.
An Indian company is not required to file the FLA Return if it does not make any FDI or ODI investments by the end of the reporting year. The FLA return must be filed every year if an Indian company has any outstanding FDI or ODI.
Annual Report on Performance
Those Indian parties or residents who have made an ODI must submit an annual performance report every year (ODI). Joint Venture, Wholly Owned Subsidiaries (WOS) outside India shall also file an Annual Performance Report in Form ODI Part II to the AD bank by December 31st each year.
Appropriate for Software Firms
- The company's directors and staff have the option of investing in Promoters Company shares in other countries (JV or WOS).
- There are only a certain number of shares available for purchasing. The authorized limit is $10,000 for a period of five calendar years.
- These shares cannot account for more than 5% of the issuing company's paid-up capital.
- Holdings after allotment should not exceed those held before allotment.
Commercial Borrowing from Outside
Borrowers must disclose all ECB transactions to the RBI via an AD Category-I bank on a monthly basis in the form of an 'ECB 2 Return.'
Form of a Single Master (W.E.F 30.06.2018)
On September 1, 2018, the Reserve Bank of India (the "RBI") released a client handbook (the "SMF Manual") to explain the system for filing a single master form (the "SMF"), which was introduced on June 7, 2018, to incorporate the current detailed standards for foreign investment in India.
The following forms can now be filled out as part of a single SMF form.
- FC-GPR- The form utilized by an Indian company to provide capital instruments to a person residing outside of India. FDI must be reported on this form within 30 days after money allocation.
- The FC-TRS form is used to transfer capital instruments from a foreign resident to an Indian person.
- Under the SMF, FC-TRS must be submitted within 60 days of transferring capital instruments or remitting cash, whichever comes first.
- LLP-I-Foreign Direct Investment, which is required by an LLP, this form is employed.
- LLP-II-This is the form that is utilized for an LLP's Divestment or Transfer of Capital Contribution.
- Convertible Notes (CN) - The form used to issue or transfer convertible notes. Convertible notes must be reported within 60 days of their transfer.
- DRR- This is the form that is used to issue depository receipt transfers.
- Employee Stock Option Plan (ESOP)- This is the form that is utilized to provide employee stock options or sweat equity shares.
- DI- Downstream investment or some sort of foreign indirect investment in a firm is reported using this form.
Form for Advance Reporting
An Indian organization that receives foreign investment for the issue of shares or other qualified securities under the FDI Scheme must report the details of the amount of consideration to the Reserve Bank's concerned Regional Office via its AD Category I bank within 30 days of the date of issue of offers.
FC-GPR (Form)
The RBI issues this form in accordance with the Foreign Exchange Management Act of 1999. When a company obtains foreign investment, it distributes its stock to outside investors in exchange for the money.
It is the responsibility of the organization to file the details of such a share allotment with the RBI within 30 days. The FC-GPR form must be used by the organization (Foreign Currency-Gross Provisional Return).
FC-TRS
Foreign Currency Transfer (FC-TRS) is the abbreviation for Foreign Currency Transfer. When shares or convertible debentures of an Indian firm are transferred from a resident to a non-resident/non-resident Indian or vice versa for sale, this form must be completed.
Form ODI
Any Indian resident or Indian organization interested in investing in the overseas market must complete Form ODI. They should also send the share certificate or proof of investment for a joint venture or fully owned subsidy to the designated AD within 30 days.
Guidelines and Features of FEMA Compliance
All forex-related offences are classified as civil offences by FEMA, but criminal ones by FERA. As a result, it might be considered one of FEMA's characteristics.
Other Important FEMA Compliance Features and Guidelines are as Follows:
- FEMA will not affect Indians who live in other countries. A technique is utilized to ascertain an Indian citizen's residency. To begin, the number of days spent in India during the preceding fiscal year is calculated (182 days or more to be a resident). An office, a branch, or an agency may be deemed a person for the purposes of calculating Indian residency.
- The Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA) grants the federal government the authority to impose restrictions on three things while also overseeing them. Payments sent to persons outside of India, payments received from India, currencies, and international security arrangements are all examples of this.
- It denotes the areas where the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) or the government must intervene in the acquisition or holding of foreign currency.
- Foreign exchange transactions are divided into two categories by the FEMA:
-
1. Capital Account.
2. Current Account.
The goal of a capital account transaction is to modify an individual's assets and liabilities whether they are located outside or inside India. As a result, every transaction that results in a change in an Indian resident's foreign assets and liabilities, or vice versa, is classified as a capital account transaction. Any other type of transaction is classified as a current account.
Who is in charge of FEMA compliance?
- The Reserve Bank of India is the major regulator of foreign exchange in India (RBI).
- The Income Tax Act would also apply to NRI/Company Accounts in terms of taxation.
- Aside from the aforementioned rules, the Companies Act of 2013 would apply to business transactions.
- Capital instruments would be subject to the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 (SEBI).
Criteria for FEMA Compliance Eligibility
FEMA services are available to the following people:
- Individuals.
- Individuals with a High Net Worth.
- Companies.
- Concerns about partnerships and sole proprietorships.
- NRIs.
- Individuals from other countries.
- Institutional investors from other countries.
Compliance Process/Procedure under FEMA
Foreign investment in India can take the form of foreign direct investment (FDI), foreign portfolio investment (FPI), or foreign direct investment (FDI) (FI). For an individual or a business, FEMA compliance is critical. Foreign direct investment (FDI) is a form of capital. As a result, they face severe consequences. The automatic route and the approved route are the two options for foreign direct investment in India. An investor's FDI is authorized to be 100 percent foreign under the automatic approach. To carry out a certain transaction, no previous authorization from the government is required.
Requirement of FEMA Compliance
For the following transactions, FEMA compliance is necessary

FEMA FDI -Automatic Route
- 100% foreign direct is permitted under the Automatic Route.
- There is no set deadline for this. However, the investor must make these investments within a certain time frame.
- There are 11 types of investments that do not require previous government clearance.
- E-Commerce, Agricultural Activities, Animal Husbandry, Health Care, Manufacturing, Textiles, Garments, and Capital Goods Sector, Plantation Sector, Petroleum and Natural Gas Sector, Minerals Sector, Non-News Current Affairs and Television Channels, Broadcasting, Construction Sector are the categories.
- Other industries require government authorization. Investment in the aforementioned sectors does not require FEMA compliance.
FDI through the Government/Approval Route
- For FDI activities in India, several sectors require prior government authorization. Investments from specific nations are also subject to government permission for FDI-based activities.
- This route does not have a specific time constraint.
- China, Bhutan, Nepal, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Pakistan, and Afghanistan are among the countries that must go through the approval process.
- The SOP (Standard Operating Procedure) form must be used to fill out the application. For the FIFP (Foreign Investment Facilitation Portal) Online, this will be required.
- The Department of Industrial Policy and Promotion (DIPP) will examine the application and send it to the RBI for FEMA compliance.
- For specific industries, other relevant authorities would be notified. An application's approval or rejection would take 6 to 8 weeks.
- For certain purposes, clearances would be necessary. Compliance with FEMA is critical for sectors that are within the government's jurisdiction.
Investment procedure
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) - Sole Proprietorship or Partnership Firm
- Non-Resident Indians (NRIs) and Persons of Indian Origin (PIOs) can participate in capital instruments through partnerships and sole proprietorships (PIO).
- These transactions can be completed at any time.
- Under the Automatic Route, investment in these business formations allows for 100% investment. However, the following rules must be followed:
- The following scenarios would necessitate government approval:
- Government clearance is not required for investment in the aforesaid corporate entities. When the applicant must repatriate investments back to their home country, FEMA compliance is critical.
1. The donation must be made on a non-returnable basis. This indicates that an investment in a sole proprietorship or partnership firm's capital instruments will not be able to be transferred back to the investor's native country. These investments would receive the same treatment as domestic investments.
2. The funds must be transferred through the NRI/ PIO's NRE/ FCNR/ NRO account. The money would be transferred through the designated bank.
3. The company that receives the investment from an NRI/PIO must not be involved in real estate or agricultural activities.
1. When the investment can be repaid.
2. When a non-resident Indian or a person of Indian origin makes an investment.
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) in Limited Liability Partnerships (LLP)
- The LLP FDI rules have been loosened. Limited Liability Partnerships are available to NRIs and PIOs.
- There are no specific time limits for carrying out investing activities.
- This type of company structure has seen significant government deregulation. FDI investment in a limited liability partnership (LLP) became subject to the automatic route in 2015. In an LLP, there are special criteria for FDI:
- In some industries, FDI is only permitted through limited-liability partnerships.
- There should be no criteria for FDI that are tied to performance.
- Designated Partners of the Limited Liability Partnership should be individuals (NRI/PIO) or foreign companies. Section 7 of the Limited Liability Partnership Act of 2008 mandates this.
- External Commercial Borrowings are an option for LLPs (ECB).
- Limited liability partnerships (LLPs) can be formed from corporations. The investments must, however, be within the prescribed sector limits and fall under the 100% automatic route.
Why Choose Us

Free Legal Advice

Transparent Pricing
On Time Delivery
Expert Team

Money Back Guarantee

200+ CA/CS Assisted

Lowest Fees

Easy EMIs
Frequently Asked Questions
The LSR plan permits a resident Indian, NRI, or foreign citizen to send up to USD 250,000 from India to other nations in a single monetary year without requiring RBI or central government clearance.
The Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA) was passed by the Indian Parliament in 1999 to "consolidate and reform the law relating to foreign exchange in order to facilitate external commerce and payments and promote the orderly development and maintenance of the foreign exchange market in India."
 9559179325
9559179325 9559179325
9559179325 9559179325
9559179325











